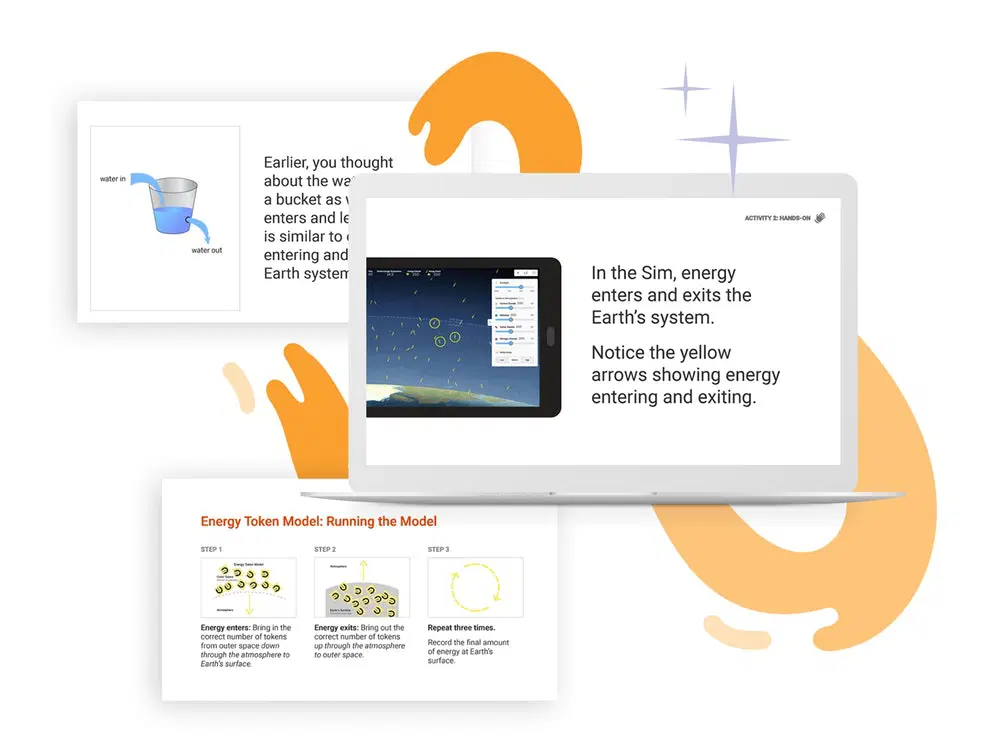
A closer look at grades 6–8 (domain)
Amplify Science is based on the latest research on teaching and learning and helps teachers deliver rigorous and riveting lessons through hands-on investigations, literacy-rich activities, and interactive digital tools that empower students to think, read, write, and argue like real scientists.
In the 6–8 classroom, this looks like students:
- Collecting evidence from a variety of sources.
- Making sense of evidence in a variety of ways.
- Formulating convincing scientific arguments.
Is your school implementing the domain model? Click here.

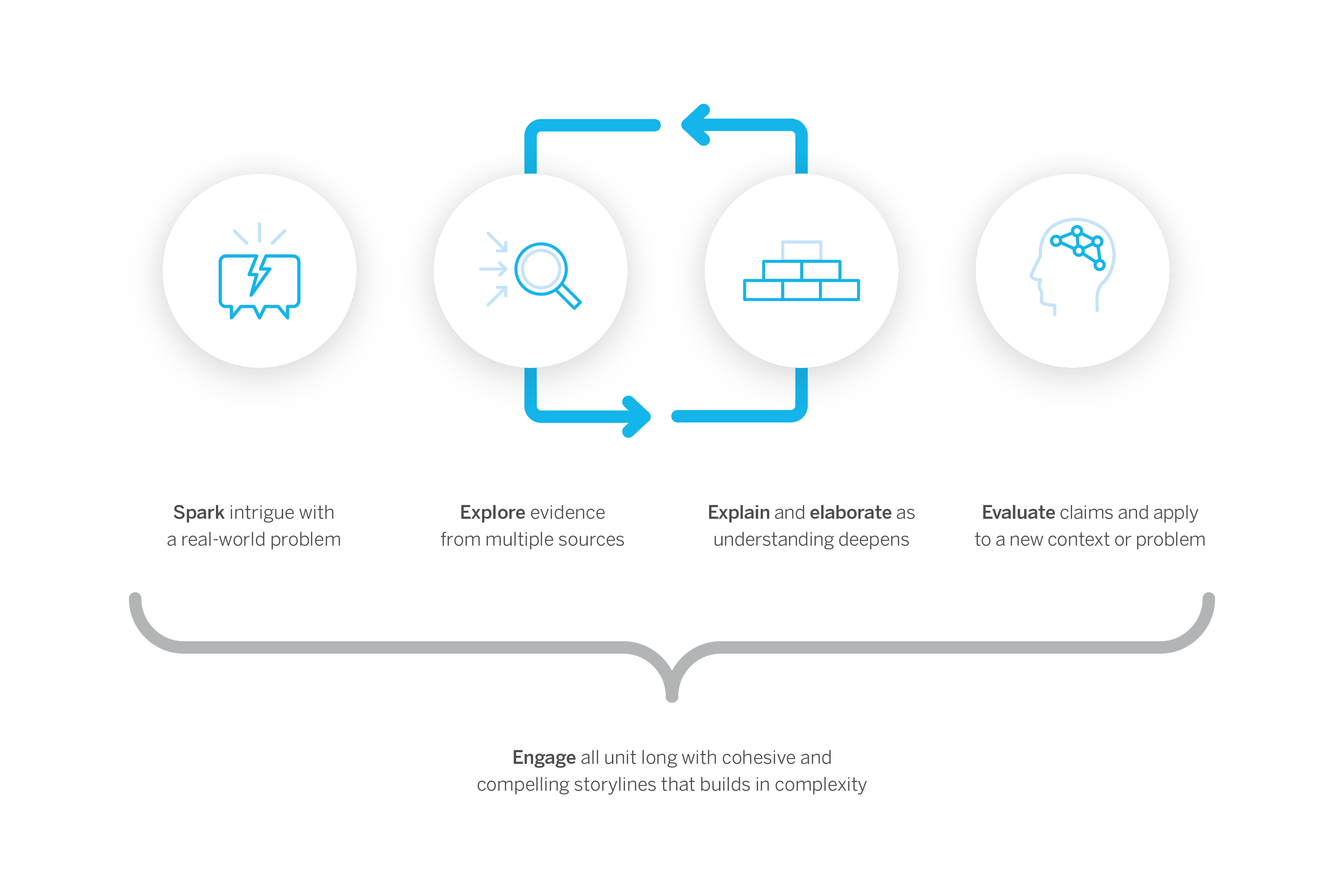
Program structure
Our cyclical lesson design ensures students receive multiple exposures to concepts through a variety of modalities. As they progress through the lessons within a unit, students build and deepen their understanding, increasing their ability to develop and refine complex explanations of the unit’s phenomenon.
It’s this proven program structure and lesson design that enables Amplify Science to teach less, but achieve more. Rather than asking teachers to wade through unnecessary content, we designed our 6–8 program to address 100% of the NGSS in fewer lessons than other programs.
Scope and sequence
Every year our grades 6–8 sequence consists of 9 units, with each unit containing 10–19 lessons. Lessons are written to last a minimum of 45-minutes, though teachers can expand or contract the timing to meet their needs.
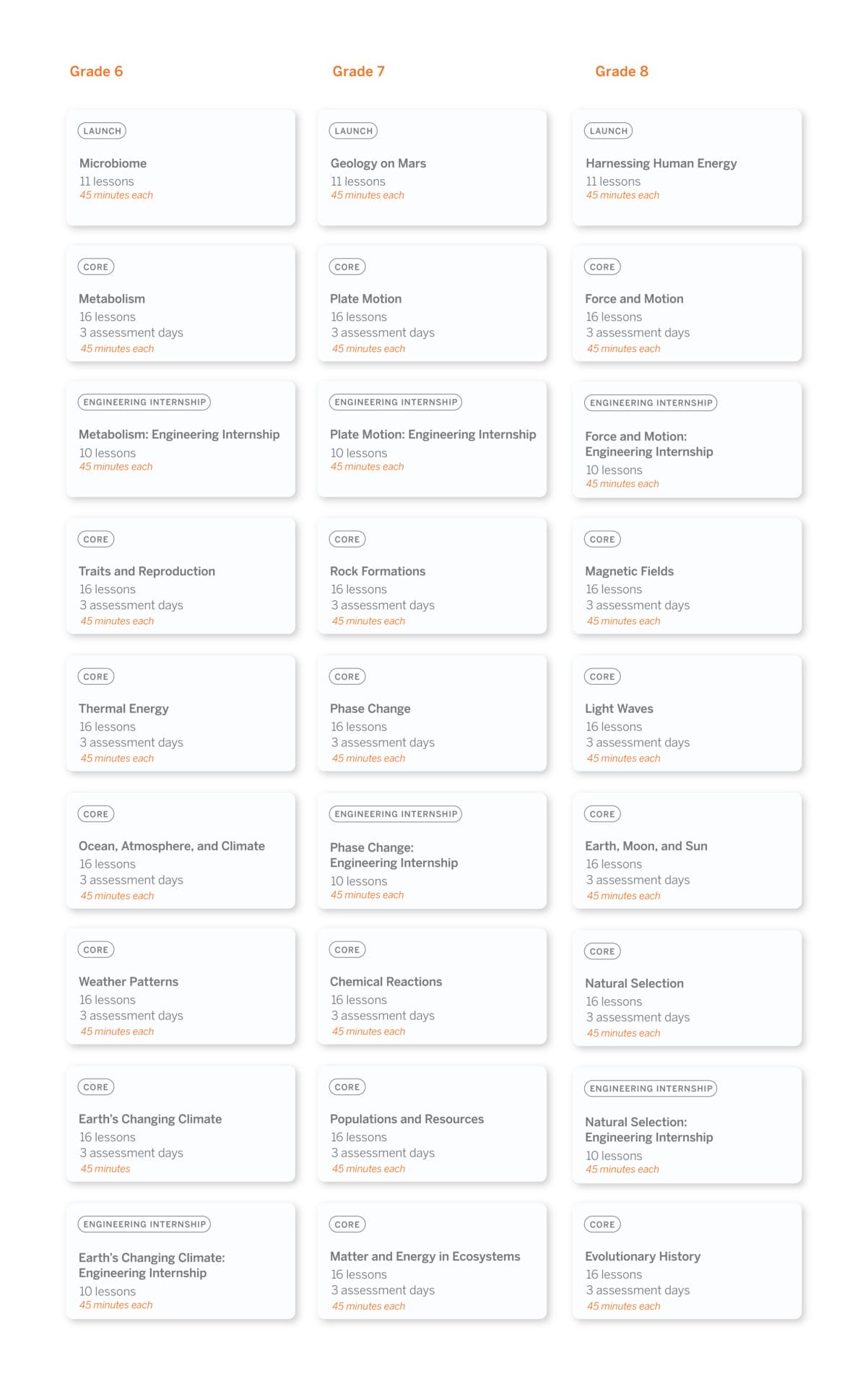
Unit types
Each unit delivers three-dimensional learning experiences and engages students in gathering evidence from a rich collection of sources, while also serving a unique purpose.
In grades 6–8, there are three types of units:
- One unit is a launch unit.
- Three units are core units.
- Two units are engineering internships.
Launch units
Launch units are the first units taught in each year of Amplify Science. The goal of the Launch unit is to introduce students to norms, routines, and practices that will be built on throughout the year, including argumentation, active reading, and using the program’s technology. For example, rather than taking the time to explain the process of active reading in every unit in a given year, it is explained thoroughly in the Launch unit, thereby preparing students to read actively in all subsequent units.
Core units
Core units establish the context of the unit by introducing students to a real-world problem. As students move through lessons in a Core unit, they figure out the unit’s anchoring phenomenon, gain an understanding of the unit’s disciplinary core ideas and science and engineering practices, and make linkages across topics through the crosscutting concepts. Each Core unit culminates with a Science Seminar and final writing activity.
Engineering Internship units
Engineering Internship units invite students to design solutions for real-world problems as interns for a fictional company called Futura. Students figure out how to help those in need, from tsunami victims in Sri Lanka to premature babies, through the application of engineering practices. In the process, they apply and deepen their learning from Core units.
Units at a glance
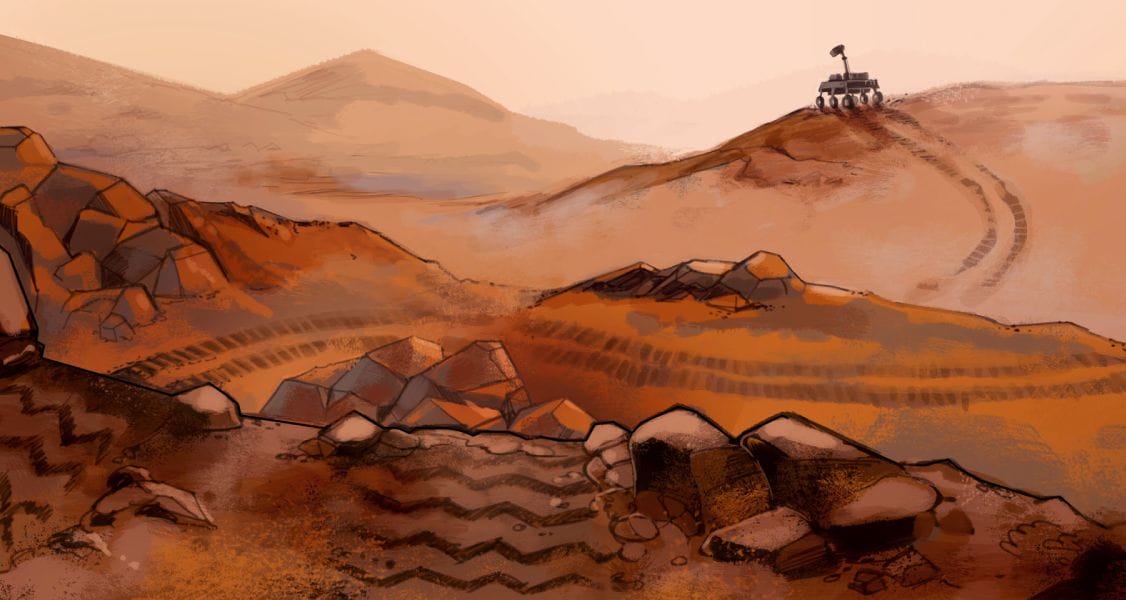

Geology on Mars
Domain: Earth and Space Science
Unit type: Launch
Student role: Planetary geologists
Phenomenon: Analyzing data about landforms on Mars can provide evidence that Mars may have once been habitable.

Plate Motion
Domain: Earth and Space Science
Unit type: Core
Student role: Geologists
Phenomenon: Mesosaurus fossils have been found on continents separated by thousands of kilometers of ocean, even though the Mesosaurus species once lived all together.

Plate Motion Engineering Internship
Domain: Earth and Space Science
Unit type: Engineering internship
Student role: Mechanical engineering interns
Phenomenon: Patterns in earthquake data can be used to design an effective tsunami warning system.

Rock Transformations
Domain: Earth and Space Science
Unit type: Core
Student role: Geologists
Phenomenon: Rock samples from the Great Plains and from the Rocky Mountains — regions hundreds of miles apart — look very different, but have surprisingly similar mineral compositions.

Earth, Sun, and Moon
Domain: Earth and Space Science
Unit type: Core
Student role: Astronomers
Phenomenon: An astrophotographer can only take pictures of specific features on the Moon at certain times.

Ocean, Atmosphere, and Climate
Domain: Earth and Space Science
Unit type: Core
Student role: Climatologists
Phenomenon: During El Niño years, the air temperature in Christchurch, New Zealand is cooler than usual.

Weather Patterns
Domain: Earth and Space Science
Unit type: Core
Student role: Forensic meteorologists
Phenomenon: In recent years, rainstorms in Galetown have been unusually severe.

Earth’s Changing Climate
Domain: Earth and Space Science
Unit type: Core
Student role: Climatologists
Phenomenon: The ice on Earth’s surface is melting.

Earth’s Changing Climate Engineering Internship
Domain: Earth and Space Science
Unit type: Engineering internship
Student role: Civil engineers
Phenomenon: Designing rooftops with different modifications can reduce a city’s impact on climate change.

Microbiome
Domain: Life Science
Unit type: Launch
Student role: Microbiological researchers
Phenomenon: The presence of 100 trillion microorganisms living on and in the human body may keep the body healthy.

Metabolism
Domain: Life Science
Unit type: Core
Student role: Medical researchers
Phenomenon: Elisa, a young patient, feels tired all the time.

Metabolism Engineering Internship
Domain: Life Science
Unit type: Engineering internship
Student role: Food engineers
Phenomenon: Designing health bars with different molecular compositions can effectively meet the metabolic needs of patients or rescue workers.

Traits and Reproduction
Domain: Life Science
Unit type: Core
Student role: Biomedical students
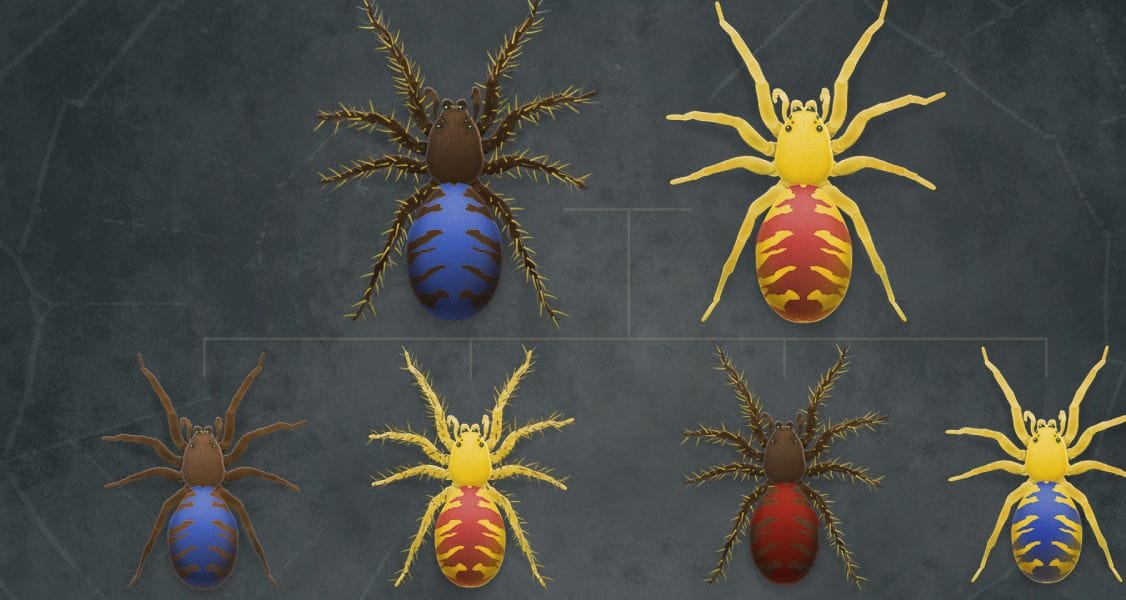
Phenomenon: Darwin’s bark spider offspring have different silk flexibility traits, even though they have the same parents.

Populations and Resources
Domain: Life Science
Unit type: Core
Student role: Biologists
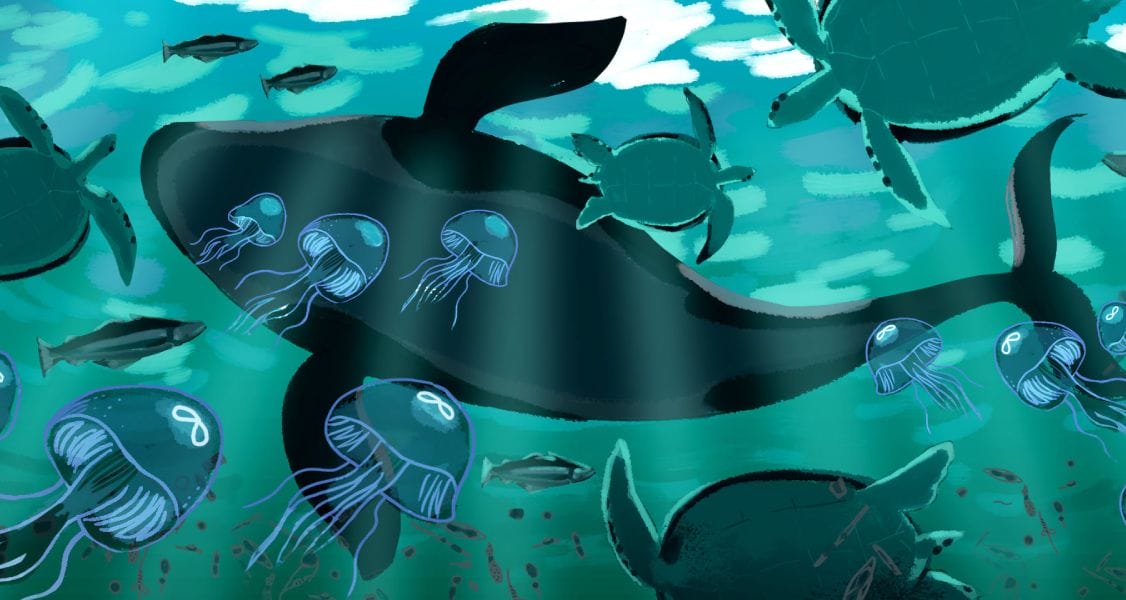
Phenomenon: The size of the moon jelly population in Glacier Sea has increased.

Matter and Energy in Ecosystems
Domain: Life Science
Unit type: Core
Student role: Ecologists
Phenomenon: What caused the mysterious crash of a biodome ecosystem?

Natural Selection
Domain: Life Science
Unit type: Core
Student role: Biologists
Phenomenon: The newt population in Oregon State Park has become more poisonous over time.

Natural Selection Engineering Internship
Domain: Life Science
Unit type: Engineering internship
Student role: Clinical engineers
Phenomenon: Designing malaria treatment plans that use different combinations of drugs can reduce drug resistance development while helping malaria patients.

Evolutionary History
Domain: Life Science
Unit type: Core
Student role: Paleontologists
Phenomenon: A mystery fossil at the Natural History Museum has similarities with both wolves and whales.

Harnessing Human Energy
Domain: Physical Science
Unit type: Launch
Student role: Energy scientists
Phenomenon: Rescue workers can use their own human kinetic energy to power the electrical devices they use during rescue missions.

Force and Motion
Domain: Physical Science
Unit type: Core
Student role: Physicists
Phenomenon: The asteroid sample-collecting pod failed to dock at the space station as planned.
Force and Motion Engineering Internship
Domain: Physical Science
Unit type: Engineering internship
Student role: Mechanical engineering interns
Phenomenon: Designing emergency supply delivery pods with different structures can maintain the integrity of the supply pods and their contents.

Magnetic Fields
Domain: Physical Science
Unit type: Core
Student role: Physicists
Phenomenon: During a test launch, a spacecraft traveled much faster than expected.

Thermal Energy
Domain: Physical Science
Unit type: Core
Student role: Thermal scientists
Phenomenon: One of two proposed heating systems for Riverdale School will best heat the school.

Phase Change
Domain: Physical Science
Unit type: Core
Student role: Chemists
Phenomenon: A methane lake on Titan no longer appears in images taken by a space probe two years apart.

Phase Change Engineering Internship
Domain: Physical Science
Unit type: Engineering internship
Student role: Chemical engineering interns
Phenomenon: Designing portable baby incubators with different combinations of phase change materials can keep babies at a healthy temperature.

Chemical Reactions
Domain: Physical Science
Unit type: Core
Student role: Forensic chemists
Phenomenon: A mysterious brown substance has been detected in the tap water of Westfield.

Light Waves
Domain: Physical Science
Unit type: Core
Student role: Spectroscopists
Phenomenon: The rate of skin cancer is higher in Australia than in other parts of the world.